The Global Nuclear Waste Crisis
Clean air and drinking water and healthy food are the very foundation of a just and livable world. They are already more precious than ever due to the climate crisis.
Nuclear power and nuclear weapons are poisoning our water, air, and lands with vast amounts of radioactive waste. Much of the harm is inflicted on Black, Indigenous, People of Color and low-income white communities, due to structural racism and injustice.
Radioactive waste poses a global environmental crisis, in tandem with climate change. The sheer amount of nuclear waste is enough to threaten clean drinking water and healthy food for the whole world.
We are on the frontlines of this problem.
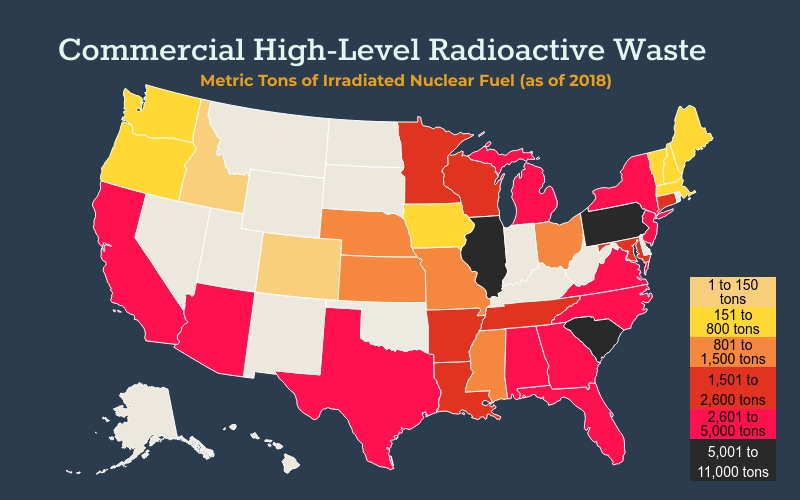
- Nearly one-third of the worldwide total of radioactive waste is in the United States.
- Some communities in the US are already losing their drinking water sources to radioactive contamination.
- Just one part of the radioactive waste in the US – irradiated nuclear fuel – contains enough radioactivity to make every drop of drinking water on Earth unsafe to consume.
We must solve the twin global crises of climate change and nuclear waste. Global warming amplifies the dangers of nuclear energy. Increasingly severe storms, flooding, sea-level rise, wildfires and other extreme events increase the risks of nuclear disasters and radioactive leaks and spills. And, in turn, the impacts of nuclear energy magnify the dangers of climate change:
- Poisoning drinking water and agricultural land on top of more frequent and severe droughts and crop failures.
- Compounding hurricane and flooding evacuations with radiological disasters.
- And causing people to lose their homes and communities permanently due to radiation.
It’s clear: we can’t afford the dangers of climate change or nuclear waste. And we certainly can’t afford them together.
The solutions to both are at hand. We must act now.
- To start, we must stop the problems from worsening: no more greenhouse gas emissions, and no more nuclear waste.
- We need to protect people and the water, air, and food we rely on from the dangers that are upon us. The climate is changing, and we need to protect people for extreme weather, drought, sea-level rise, and food supply disruptions. And we must safeguard our water, air, and land by securing and storing nuclear waste and toxic materials as safely as possible.
- And, we need to repair the damage and make our world healthy and vibrant again: restoring communities that have been dislocated or polluted, and cleaning up the air, land, and water so we can all thrive, for generations to come.

The Nuclear Waste Crisis At-a-Glance
|
High-Level Waste (2018) |
USA |
USA Radioactivity (curies) |
Global |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irradiated Nuclear Fuel | 82,358 tons | 15.6 billion | 246,686 tons |
| Reprocessing Waste | 14,000 tons | 60,000 | |
| Greater-than-Class-C Waste (GTCC) | 130 m3 | unknown | |
|
Uranium Waste |
USA |
Global |
|
| Abandoned Uranium Mines | 15,000+ | unknown | |
| Mill Tailings | 235 million tons | 2,353 million tons | |
| Depleted Uranium | 480,000 tons | 1,188,573 tons | |
|
Other Nuclear Waste |
USA |
Global |
|
| “Low-Level” Radioactive Waste | 22.3 million m3 | 34.8 million m3 | |
| Plutonium & Transuranic Isotopes | 158,130 m3 | unknown | |
| Nuclear Warheads | 6,185 | 13,895 |
Nuclear Waste Legislation in Congress (2019-2020)
| Bill Number | Title | Purpose | Status & Date | NIRS Position |
| H.R.2699 / S.2917 |
Nuclear Waste Policy Amendments Act of 2019 | — Restart Yucca Mountain Project
— Authorize DOE to institute CIS immediately |
11/20/2019: Reported by House Energy & Commerce Committee | Oppose |
| S.1234 | Nuclear Waste Administration Act of 2019 | — Authorize DOE to institute CIS immediately
— Starts new repository siting project |
6/27/2019: Hearing in Senate Energy & Natural Resources Committee | Oppose |
| H.R.2995 | Spent Fuel Prioritization Act of 2019 | — Prioritizes CIS for waste at certain reactor sites | 5/24/2019: Referred to House Subcommittee on Environmenta and Climate Change | Oppose |
| H.R.3136 | Storage and Transportation Of Residual and Excess Nuclear Fuel Act of 2019 | — Prioritizes CIS for waste at certain reactor sites | 6/6/2019: Referred to House Subcommittee on Environmenta and Climate Change | Oppose |
Proposed Nuclear Waste Facilities
| Project Name |
Type of Facility | Location | Capacity (metric tons) |
Owner/ Developer |
Status |
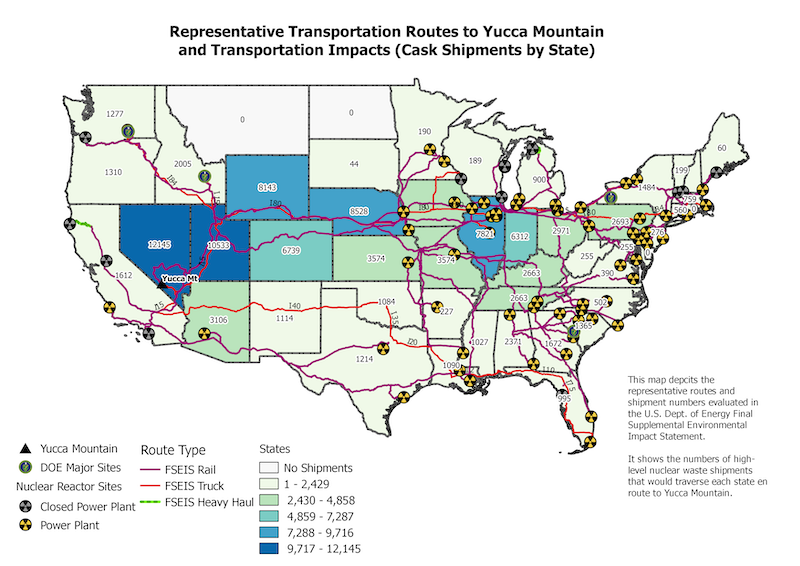
| Yucca Mountain Project | Repository | Nevada | 70,000 | U.S. Dept. of Energy | Licensing Stalled, Project Defunded |
| Interim Storage Partners | Centralized Interim Storage | Andrews County, Texas | 40,000 | Waste Control Specialists & Orano |
Licensing Review |
| Holtec International – HI-STORE CISF |
Centralized Interim Storage | Lea County, New Mexico | 170,000 | Holtec Intl. | Licensing Review |
| Deep Isolation | Borehole Repository | TBA | TBA | Deep Isolation | Research & Development |
Resources
The World Nuclear Waste Report 2019 – Heinrich Boell Foundation (2019)
The Global Crisis of Nuclear Waste – Greenpeace (2019)
Uranium Mining and Fuel Chain Waste
- Uranium Atlas: Facts and Data about the Raw Material of the Atomic Age – Rosa Luxemberg Foundation (2019)
- Worldwide Data on Uranium Mining and Nuclear Fuel Production
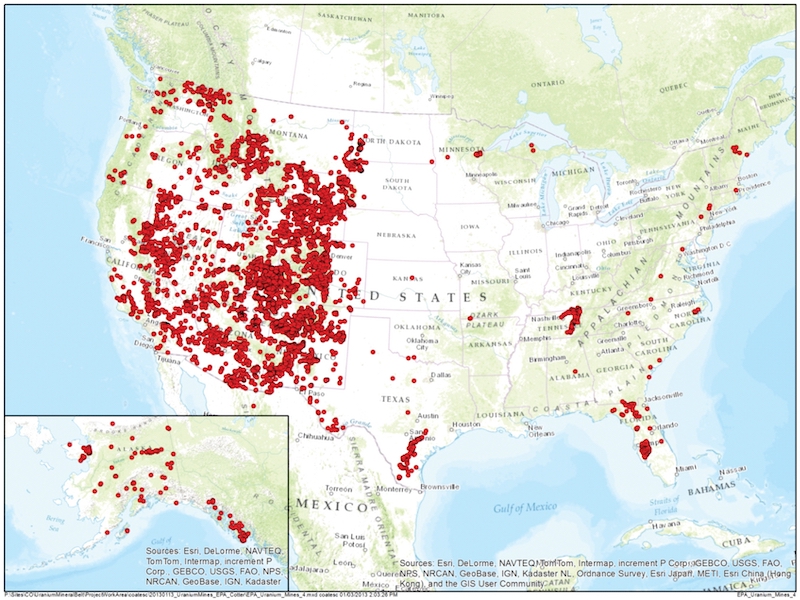
- Abandoned Uranium Mines in the US
Nuclear Power and Climate Change
- Nuclear Power and Climate Action: An Assessment for the Future – NIRS for Rosa Luxemburg Foundation (2018)
- World Nuclear Industry Status Report 2019
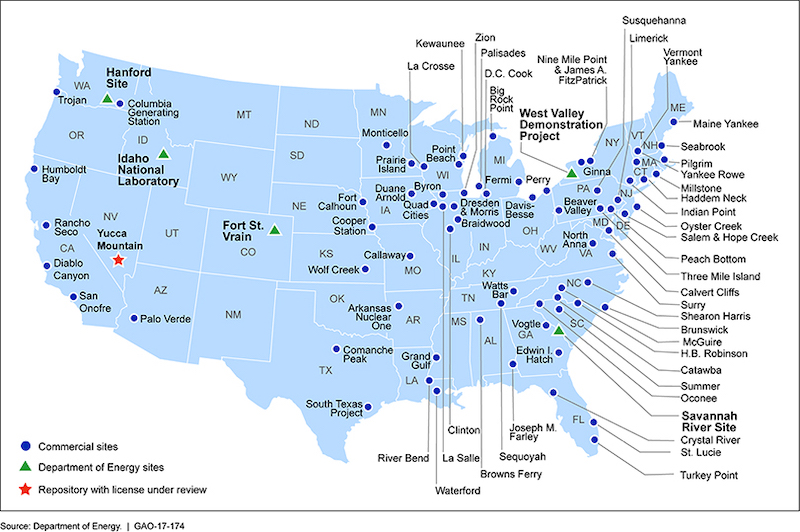
Spent Nuclear Fuel in the U.S.
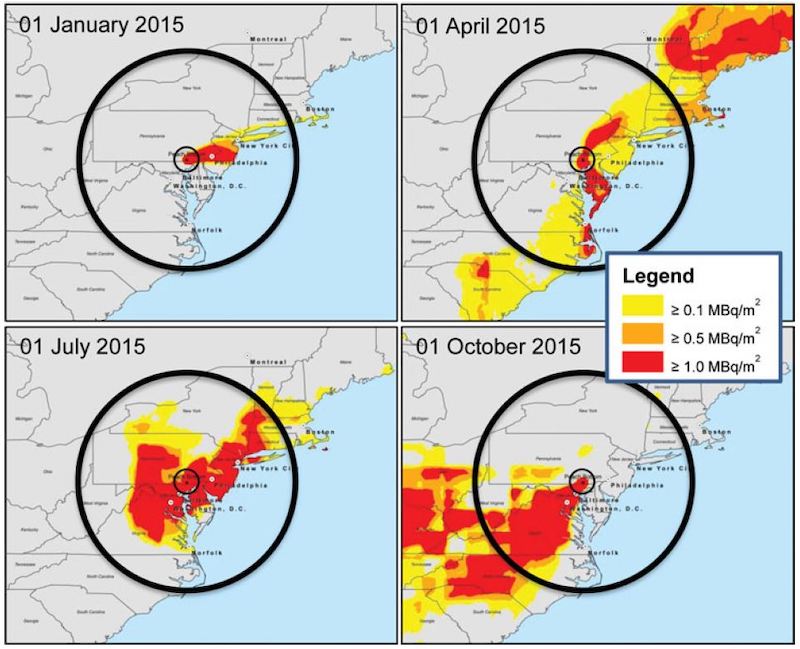
- Reducing the Danger from Fires in Spent Fuel Pools
- Robust Storage of Spent Nuclear Fuel
More Useful Maps